So on the recent Monday , the class has ventured to
the last topic of Microeconomics which is
Market Structures. We had go trough initial subtopic in the market
structure to have better acknowledgement in the particular field.
Market
structure
Definition:
- Market is a place where the buyers and sellers meet one another to transact business .
- Market also be defined as an arrangement that facilitates the buying and selling of a product, service, factor of production or future commitment.
- Market structure means the number and distribution size of buyers and sellers in the market of particular goods and services.
Profit maximization in perfect
competition market.
Market
equilibrium is achieved when the marginal cost equal to marginal revenue. Price
is determined based on the average revenue. Prices are fixed in perfect
competition, so marginal revenue is still the same result at a price.
MR=MC
P=AR=MR
Imperfect
competition such as monopolistic, monopoly and oligopoly achieved market equilibrium when marginal revenue equal
with marginal cost. Price are differentiated based on quantity supplied.
MR=MC
P=AR
Types of profit possibilities:
- Supernormal profit.
The profit earned when total revenue is greater than total cost. It also
realized when the price is greater than average total cost.
- Subnormal profit
Economic losses are the
losses incurred because the price is lower than the average total cost or when
total revenue is less than total cost.
- Normal profit
Perfect competition market.
What is perfect competition markets ?
Market in which there are a large number
of buyers and sellers, buying and selling the homogenous products at certain
price levels.
Characteristics.
A) Large number of buyers
There are many buyers in
the market but they cannot control prices. Price is fixed in the market through
the forces of demand and supply. No matter how much has been purchased, price
is always constants. Buyers are said to be price takers.
B) Many sellers in the market
There are many sellers in
the market. Like the buyers they too cannot control price. They are also price
takers. Usually the sellers are small firms. The action of one firm will affect
to the others firms. Example, if the sellers offers a lower price, then he will
incur a loss, and if he sells at a higher price, there will be no demand. In
simplicity, he is powerless in determining price but he can set the quantity he
wants to sell.
C) The product are homogeneous
The goods are homogeneous
and not differentiated. They are identical. The consumer cannot differentiate
whether the goods come from producer A or B or C. Ads is totally absent in this market.
D) Free entry to and exit from the
market.
There must be free entry
to and exit from the market. If the industry is making profits, then new firms
will enter the market. No restriction is imposed.
E) Perfect knowledge
Consumers and producers
have perfect knowledge about the market
situation.
F) Mobility of factors of production.
There must be mobility of
factors of production. There are no barriers to mobility. Land has its own
alternative uses.
G) No transportation cost.
There must be no transportation cost. It is assumed that all firms are situated close to one
another and are very close to the market.
H) Independence in decision making.
There will be no external forces that
will influence the decision of buyers and seller. They make their own
decisions.
Short run profit in perfect competition market.
In the short term,
perfect competition market has three types of profit which is:
a) Supernormal profit in perfect
competition market.
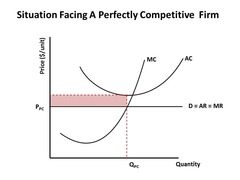
- The profit maximization occurs when marginal cost equal to marginal revenue.
- The firm earns supernormal profit when average revenue (AR) is greater than average cost (AC).
- The shaded area (EABP) is shown the profit (supernormal profit) area.
- Calculation:
TR=AR x Q
TR=P (x) x Q (y)
TR= xy
TC=AC x Q
TC=AC (a) x Q (b)
TC= ab
b) Normal profit in perfect competition
market.
- The profit maximization occurs when marginal cost equal marginal revenue .
- The firm earns normal profit when average revenue (AR) is equal with average cost (AC). Price is equal at minimum AC, firm at breakeven profit.
- So, the firm will get the normal profit because total revenue is equal with total cost.
- Calculation:
TR=AR x Q
TR=P (x)
x Q (y)
TR= xy
TR= xy
TC=AC x Q
TC=AC (x) x Q (y)
TC= xy
Therefore ,
Profit= TR – TC
=xy - xy
=0
=breakeven
=Normal profit
=Normal profit
c) Subnormal profit in perfect
competition market.
- The profit maximization occurs when marginal cost equal marginal revenue.
- The firm earns subnormal profit when average revenue (AR) is less than average cost (AC).
- So, the firm will get the subnormal profit because total revenue is less than total cost.
- The shaded (EPAB)is shown the subnormal profit (losses) area.
- Calculation:
TR=P (x)
x Q (y)
TR= xy
TC=AC x Q
TC=AC (x) x Q (y²)
TC= xy²
Therefore ,
Profit= TR – TC
=xy – xy²
= -xy
=losses
=subnormal profit